Guided implant surgery is an advanced dental procedure using 3D imaging and digital planning to ensure precise implant placement, enhancing accuracy and patient comfort significantly.
1.1. Definition and Overview
Guided implant surgery is a modern dental procedure that combines advanced technologies to enhance the precision and predictability of dental implant placement. It involves the use of three-dimensional imaging, such as Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), and computer-aided design (CAD) software to create detailed surgical guides. These guides are tailored to the patient’s anatomy, ensuring implants are placed in the optimal position for functionality and aesthetics. The process minimizes invasiveness and reduces recovery time, making it a preferred choice for both patients and surgeons. By integrating digital planning and precise execution, guided implant surgery offers a high level of accuracy, improving overall outcomes and patient satisfaction. This approach has revolutionized traditional implant placement methods, setting a new standard in modern dentistry.
1.2. Importance in Modern Dentistry
Guided implant surgery has become a cornerstone in modern dentistry due to its ability to enhance precision, reduce complications, and improve patient outcomes. By leveraging advanced technologies like 3D imaging and surgical guides, dentists can achieve highly accurate implant placements, minimizing the risk of errors. This method is particularly valuable for complex cases, such as patients with limited bone density or anatomical challenges. The use of digital planning ensures that implants are placed in optimal positions for both functionality and aesthetics, leading to higher success rates and patient satisfaction. Additionally, guided surgery often results in shorter recovery times and less post-operative discomfort, making it a preferred option for many patients. Its adoption reflects the growing emphasis on precision and minimally invasive techniques in contemporary dental practice.
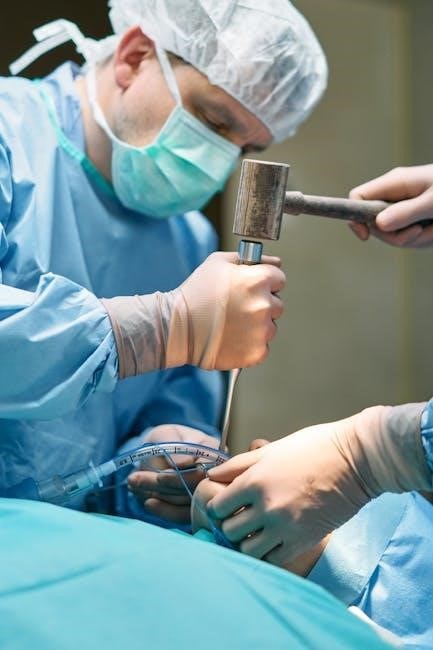
Technology Behind Guided Implant Surgery
Guided implant surgery relies on advanced technologies like Cone Beam CT (CBCT) for precise imaging and surgical guides for accurate implant placement, ensuring optimal results.
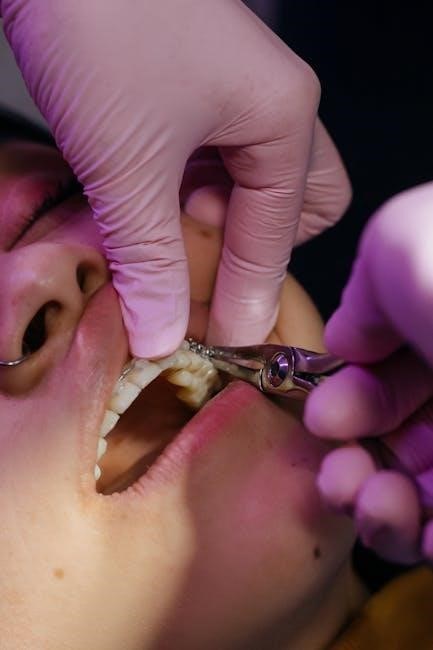
2.1. Role of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) plays a pivotal role in guided implant surgery by providing high-resolution 3D images of the jawbone, teeth, and surrounding tissues. This technology allows dentists to accurately assess bone density, identify anatomical landmarks, and plan implant placement with precision. CBCT scans help in detecting critical structures like nerves and sinus cavities, ensuring implants are placed safely and effectively. The detailed imagery enables surgeons to measure the exact dimensions of the implant site, minimizing the risk of complications. By integrating CBCT data into surgical guides, the procedure becomes more predictable and efficient, leading to better patient outcomes. This advanced imaging is a cornerstone of modern implant surgery, enhancing both accuracy and safety.
- Provides 3D visualization of anatomical structures.
- Helps in precise measurement and planning.
- Reduces risk of complications by identifying critical areas.
2.2. Use of Surgical Guides and Templates
Surgical guides and templates are custom-made tools used in guided implant surgery to translate digital plans into precise implant placement. These guides, often created using 3D printing, are designed based on CBCT scans and surgical planning software. They fit snugly over the patient’s teeth or gums, providing exact positioning for drill holes and implants. Surgical guides ensure that implants are placed at the correct angle, depth, and location, minimizing the risk of errors. They also help maintain soft tissue integrity, reducing trauma to the surrounding area. This level of precision not only enhances accuracy but also contributes to a minimally invasive procedure, improving patient comfort and reducing recovery time. The use of these guides is a key factor in the success of guided implant surgery.
- Custom-made for precise implant placement.
- Created using 3D printing technology.
- Minimizes surgical errors and tissue damage.

Benefits of Guided Implant Surgery
Guided implant surgery offers enhanced accuracy, predictability, and patient comfort. It minimizes tissue damage, reduces recovery time, and improves overall surgical outcomes and efficiency significantly.
3.1. Increased Accuracy and Precision
Guided implant surgery significantly enhances accuracy and precision by utilizing advanced imaging technologies like CBCT scans. These tools allow surgeons to create detailed 3D models of the patient’s jaw, ensuring implants are placed in optimal positions. The use of surgical guides, fabricated from precise digital plans, minimizes human error and ensures that implants are inserted exactly as planned; This level of precision not only improves the aesthetic outcomes but also ensures better functional results, leading to higher patient satisfaction and longevity of the implants. The integration of digital planning and real-time guidance during surgery further elevates the accuracy, making guided implant surgery a highly reliable option for patients.
3.2. Reduced Healing Time and Recovery
Guided implant surgery often results in shorter healing times and faster recovery for patients. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure, combined with precise implant placement, reduces tissue trauma and post-surgical discomfort. By using detailed digital plans and surgical guides, surgeons can avoid unnecessary incisions and bone preparation, minimizing the body’s recovery workload. This approach also lowers the risk of complications, such as swelling or infection, which can delay healing. Patients typically experience less pain and resume their normal activities sooner compared to traditional methods. The accuracy of guided surgery ensures optimal implant positioning, promoting faster osseointegration and long-term success.
3.3. Minimally Invasive Procedure
Guided implant surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that reduces tissue trauma and promotes faster recovery. By using precise digital planning and surgical guides, surgeons can avoid unnecessary incisions and bone preparation; This approach minimizes disruption to surrounding tissues, leading to less post-operative discomfort and swelling. The use of advanced imaging ensures that implants are placed accurately without compromising adjacent structures. Additionally, the minimally invasive nature of the procedure often eliminates the need for extensive suturing, further reducing healing time. Patients benefit from a less traumatic experience, making guided implant surgery a more appealing option compared to traditional methods.
The Process of Guided Implant Surgery
Guided implant surgery involves detailed pre-surgical planning, fabrication of precise surgical guides, and accurate execution, optimizing implant placement and minimizing recovery time.
4.1. Pre-Surgical Planning and Imaging
Pre-surgical planning is the cornerstone of guided implant surgery, utilizing advanced imaging techniques like CBCT scans to create detailed 3D models of the patient’s jawbone and surrounding tissues. These images allow dentists to identify anatomical structures, such as nerves and sinuses, ensuring precise implant placement. Specialized software is used to analyze the data, enabling the creation of a digital treatment plan. This step involves determining the optimal implant position, angle, and depth to achieve both functional and aesthetic outcomes. The integration of digital models and surgical guides ensures a high level of accuracy, minimizing risks and improving predictability. This meticulous planning phase sets the foundation for a successful and efficient surgical procedure.
4.2; Surgical Guide Fabrication
Surgical guides are custom-made templates created from the pre-surgical planning data, ensuring precise implant placement. These guides are typically fabricated using 3D printing technology, which offers high accuracy and detail. The guides are designed to fit the patient’s jaw anatomy perfectly, with drill holes that direct the surgeon to the exact implant locations, angles, and depths planned during the pre-surgical phase. This step ensures that the implants are placed in optimal positions, avoiding critical structures such as nerves and sinuses. The use of surgical guides minimizes human error and enhances the predictability of the procedure. Once fabricated, the guides are sterilized and prepared for use during the actual surgery, serving as a critical tool for achieving successful outcomes.
4.3. Execution of the Surgery
During the execution of guided implant surgery, the pre-fabricated surgical guide is securely placed over the patient’s jaw to direct the surgeon’s instruments. Local anesthesia is administered to ensure patient comfort. The surgeon uses the guide’s predefined drill holes to create precise pilot openings in the bone, following the planned depth and angle. The implants are then carefully inserted into these prepared sites, ensuring optimal alignment and stability. Once all implants are placed, the surgical sites are cleaned, and healing caps or abutments are attached. The procedure typically results in minimal bleeding and trauma, promoting faster recovery. Post-surgery, the patient is monitored for a short period before being discharged with specific aftercare instructions.
Advantages Over Traditional Implant Surgery
Guided implant surgery offers enhanced accuracy, reduced invasiveness, and faster recovery compared to traditional methods. It minimizes tissue damage and improves surgical predictability.
5.1. Improved Patient Outcomes
Guided implant surgery significantly enhances patient outcomes by ensuring precise implant placement, reducing complications, and promoting faster recovery. The use of 3D imaging and digital planning allows for customized procedures, improving aesthetic and functional results. Patients experience less discomfort and swelling due to minimally invasive techniques. Additionally, the accuracy of guided surgery minimizes the risk of nerve damage or misplacement, leading to higher satisfaction rates. Overall, this advanced method delivers predictable and optimal results, making it a preferred choice for patients seeking reliable dental implant solutions.
5.2. Reduced Risk of Complications
Guided implant surgery significantly reduces the risk of complications compared to traditional methods. The use of 3D imaging and digital planning ensures precise implant placement, minimizing the chance of nerve damage or incorrect positioning. Surgical guides prevent deviations during the procedure, lowering the likelihood of complications such as bone perforation or inadequate osseointegration. Additionally, the minimally invasive nature of guided surgery reduces tissue trauma, lowering the risk of post-operative infections or prolonged healing times. Overall, this approach enhances safety and reliability, making it a preferred method for minimizing complications and ensuring successful implant placement.
Guided implant surgery has revolutionized dental implant placement by combining advanced technologies with precise surgical techniques. Its reliance on 3D imaging and digital planning ensures high accuracy, minimizes complications, and enhances patient outcomes. By reducing healing times and offering a minimally invasive approach, this method has become a preferred choice for both patients and dentists. The integration of cone beam CT scans and surgical guides has set a new standard in modern dentistry, making implant surgery safer and more predictable. As technology continues to evolve, guided implant surgery is poised to remain a cornerstone in achieving optimal results for patients seeking durable and aesthetically pleasing dental restorations.
